Citrix XenServer is a server virtualization platform that virtualizes business critical workloads and enables datacenters to be flexible and dynamic. XenServer serves as the foundation for most Citrix virtualization solutions, therefore it is critical that you know how XenServer works and how it integrates with other component technologies.
Citrix solution overview
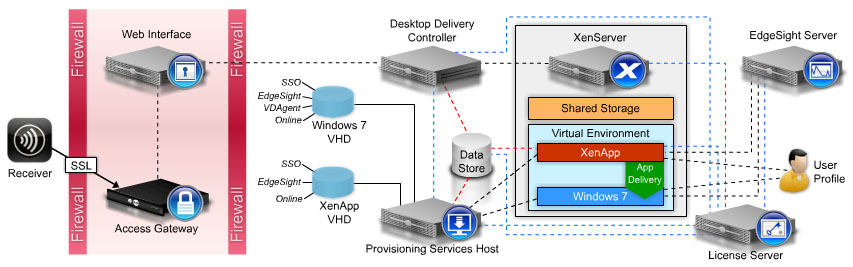
The XenServer environment provides the foundation for the entire virtualization infrastructure on which the CVE-401 lab environment is built. In this lab environment, we will be working with a single XenServer host and storage repository. However, in production deployments you will need to consider shared storage architectures, networking, and ISO repositories.
In all cases, you will need a Citrix License Server to allow the XenServer host to validate the required license. The License Server used to store the XenServer licenses can be the same license server that is used for other Citrix products.
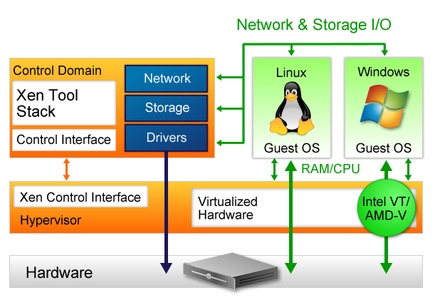
XenServer Architecture - You can use Citrix XenServer in an end-to-end virtualization solution to dramatically reduce the datacentre footprint and simplify server management. XenServer is a bare metal hypervisor that includes features such as live migration, shared storage support, and centralized muiti server management with Physical to Virtual and Virtual to Virtual (P2V and V2V) conversion tools.
An ISO library is a central network share that stores ISO images. You can store a XenServer ISO library on either a CIFS or NFS tile share, depending on which storage solution is available for your environment and which solution has sufficient storage space for the ISO library. You must consider the following when configuring an ISO library storage solution:
Pre-installation Considerations:
- Configure local storage for RAID or boot from SAN (adds more complexity)
- Configure the network for fault tolerance: Multiple NICs, Cables (disconnected / damaged), Switches (PSU failure / FW upgrade)
- Enable hardware virtualization - Windows might not run properly, update BIOS to the latest version to eliminate false warning
- Decide on the XenServer installation method - CD, PXE w TFTP or NFS share
- Decide on the type of storage - Local, SAN (FC or iSCSI), NFS; virtual disks are stored in Microsoft VHD format
- Secure the virtual environment
- Ensure that licenses are updated and available - XenServer Licensing FAQ - http://support.citrix.com/article/CTX125301
The license server used to store XenServer licenses can be the same server that is used for other Citrix products.
RAID Configuration - If local storage is being used, ensure redundancy at the disk level by configuring the XenServer host for redundant array of independent disks (RAID). You can configure a XenServer host to start from SAN, if it is available. This provides redundancy at the disk level but adds more complexity than using local storage on the XenServer host.
Network Fault Tolerance Considerations - You can improve network resiliency by ensuring redundancy at all network infrastructure levels. Consider the following network failure points when planning for fault tolerance:
• Network Interface Card (NIC)
• Network cable (for example, if it is disconnected or damaged)
• Switch (for example, if the power supply fails) - You might also need to take switches offline for planned outages, such as firmware upgrades.
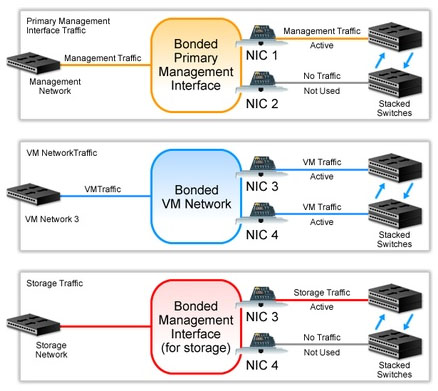
Bonded NICs - When considering whether or not to bond NICs, balance your requirement for redundancy and load balancing with the number of separate subnets and VLANs each resource pool requires. Depending on your redundancy requirements, you can connect bonded NICs to the same or separate switches. If you link bonded NICs to separate switches, you will mitigate the impact of switch failure. You must run the switches in a stacked configuration, in which the switches are configured to function as a single switch that is seen as a single domain
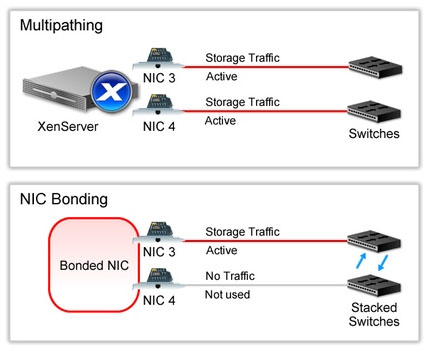
Multipathing - allows storage traffic to be routed over multiple paths for redundancy and increased throughput. Multipathing is an active-
active configuration which uses round-robin mode load balancing, so both routes will have active traffic during normal operation.
Citrix recommends that:
- you do not mix NIC bonding and iSCSI multipathing
- you enable multipathing instead of using NIC bonding whenever possible. Multipathing enables better performance and provides failover support; bonding does not provide failover support
You should consider using NIC bonding instead of multipathing when:
• You are configuring an NFS storage device.
• Your storage device does not support iSCSI connections over multiple IPs.
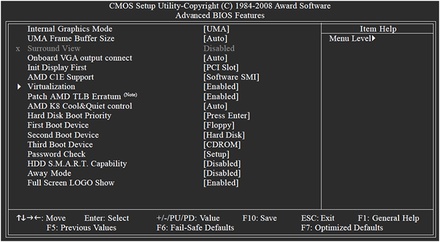
Hardware Virtualisation - You must enable hardware virtualization in the BIOS to install XenServer.
Citrix solution overview

The XenServer environment provides the foundation for the entire virtualization infrastructure on which the CVE-401 lab environment is built. In this lab environment, we will be working with a single XenServer host and storage repository. However, in production deployments you will need to consider shared storage architectures, networking, and ISO repositories.
In all cases, you will need a Citrix License Server to allow the XenServer host to validate the required license. The License Server used to store the XenServer licenses can be the same license server that is used for other Citrix products.
XenServer Architecture - You can use Citrix XenServer in an end-to-end virtualization solution to dramatically reduce the datacentre footprint and simplify server management. XenServer is a bare metal hypervisor that includes features such as live migration, shared storage support, and centralized muiti server management with Physical to Virtual and Virtual to Virtual (P2V and V2V) conversion tools.

An ISO library is a central network share that stores ISO images. You can store a XenServer ISO library on either a CIFS or NFS tile share, depending on which storage solution is available for your environment and which solution has sufficient storage space for the ISO library. You must consider the following when configuring an ISO library storage solution:
- Number of ISOs in the library
- Number of ISO libraries
- Number of simultaneous connections to the library: A constant connection is maintained to the ISO library for each default ISO file that is assigned to a virtual machine in the XenCenter console. As the number of virtual machines in the environment increases over time, the number of connections to this ISO library increases as well. You must verify that the CIFS or NFS server can handle the volume of simultaneous connections to the library to avoid poor performance.
- Number of ISO libraries
- Number of simultaneous connections to the library: A constant connection is maintained to the ISO library for each default ISO file that is assigned to a virtual machine in the XenCenter console. As the number of virtual machines in the environment increases over time, the number of connections to this ISO library increases as well. You must verify that the CIFS or NFS server can handle the volume of simultaneous connections to the library to avoid poor performance.
- Configure local storage for RAID or boot from SAN (adds more complexity)
- Configure the network for fault tolerance: Multiple NICs, Cables (disconnected / damaged), Switches (PSU failure / FW upgrade)
- Enable hardware virtualization - Windows might not run properly, update BIOS to the latest version to eliminate false warning
- Decide on the XenServer installation method - CD, PXE w TFTP or NFS share
- Decide on the type of storage - Local, SAN (FC or iSCSI), NFS; virtual disks are stored in Microsoft VHD format
- Secure the virtual environment
- Ensure that licenses are updated and available - XenServer Licensing FAQ - http://support.citrix.com/article/CTX125301
The license server used to store XenServer licenses can be the same server that is used for other Citrix products.
RAID Configuration - If local storage is being used, ensure redundancy at the disk level by configuring the XenServer host for redundant array of independent disks (RAID). You can configure a XenServer host to start from SAN, if it is available. This provides redundancy at the disk level but adds more complexity than using local storage on the XenServer host.
Network Fault Tolerance Considerations - You can improve network resiliency by ensuring redundancy at all network infrastructure levels. Consider the following network failure points when planning for fault tolerance:
• Network Interface Card (NIC)
• Network cable (for example, if it is disconnected or damaged)
• Switch (for example, if the power supply fails) - You might also need to take switches offline for planned outages, such as firmware upgrades.
Bonded NICs - When considering whether or not to bond NICs, balance your requirement for redundancy and load balancing with the number of separate subnets and VLANs each resource pool requires. Depending on your redundancy requirements, you can connect bonded NICs to the same or separate switches. If you link bonded NICs to separate switches, you will mitigate the impact of switch failure. You must run the switches in a stacked configuration, in which the switches are configured to function as a single switch that is seen as a single domain

Multipathing - allows storage traffic to be routed over multiple paths for redundancy and increased throughput. Multipathing is an active-
active configuration which uses round-robin mode load balancing, so both routes will have active traffic during normal operation.
Citrix recommends that:
- you do not mix NIC bonding and iSCSI multipathing
- you enable multipathing instead of using NIC bonding whenever possible. Multipathing enables better performance and provides failover support; bonding does not provide failover support
You should consider using NIC bonding instead of multipathing when:
• You are configuring an NFS storage device.
• Your storage device does not support iSCSI connections over multiple IPs.

Hardware Virtualisation - You must enable hardware virtualization in the BIOS to install XenServer.

Hardware virtualization can be enabled by default depending on the hardware platform in use on the XenServer host. If hardware virtualization is not enabled or supported by the CPU, a warning message will appear during installation stating that Windows virtual machines might not run properly. Linux virtual machines do not require hardware virtualization to run on XenServer hosts. Prior to installing XenServer, it is important that you update the XenServer host BIOS to the latest version offered by the manufacturer. Use of older versions of BIOS can result in a false warning about a lack of hardware virtualization support. If this occurs, restart the XenServer host or check the support site of the hardware manufacturer for a BIOS upgrade and restart the installation.
Installation Methods - You can install XenServer using an installation CD or by setting up a network-accessible TFTP server to deliver the installation files to PXE-capable XenServer hosts. The installation CD contains the necessary packages to set up the XenServer host and to create Windows virtual machines.
Note: A TFTP installation would be preferable in a situation in which hosted datacenters do not always have access to CD-ROMs.
XenServer Storage - Introduction to Storage Technologies - http://support.citrix.com/article/CTX118397
Intellicache - Using XenServer with IntelliCache reduces the cost of hosted XenDesktop deployments by enabling the use of a combination of shared storage and local storage. It works by caching data from a virtual machine's parent VDI in local storage on the virtual machine host. This local cache is then populated as data and read from the parent VDI. When many virtual machines share a common parent VDI, the data pulled into the cache from one virtual machine can be used by another virtual machine. Therefore, further access to the master image on shared storage is not required.
The requirements for using IntelliCache are:
- A thin-provisioned, local storage repository, which is configured during XenServer installation by selecting Optimized storage on XenDesktop for thin provisioning
- An NFS- or EXT-based shared storage to host the source virtual disk image
Note: Using IntelliCache prevents XenServer hosts in the environment from using XenMotion. This feature is only supported when using XenServer with XenDesktop - XenServer 6.0 Installation Guide - http://support.citrix.com/article/CTX130421
Security Considerations - It is common for the network interfaces on a XenServer host to be configured separately for the administration, storage, and virtual machine networks. You should consider the following security modifications for each of these networks:
- Administration Network: XenCenter exclusively uses port 443 to ensure that all traffic to and from the XenServer host is SSL encrypted. Third-party XenAPI clients can be configured to use port 80, which is not encrypted. To ensure that all traffic is encrypted, add firewall rules to the administration router to block external requests from port 80 to the XenServer host.
- Storage Network: Storage traffic for IP-based solutions, such as NFS or iSCSI, is not encrypted and travels through the control domain. Traffic on the storage network should be isolated from the administration network by configuring the storage network on a separate network interface, or separate VLAN.
- Virtual Machine Network: Virtual machine traffic should be isolated from management traffic and storage traffic whenever possible. This can be done with physical NIC separation or VLAN separation.
License Configuration - XenServer supports Citrix centralized licensing for all paid editions of the product License allocation is managed centrally and enforced by a standalone Citrix License Server. You can centralize licensing for all Citrix products, and. through the License Management Console, view the entitlement and current allotment of licenses for all Citrix products. For more information about XenServer licensing, see CTX125301
Optimizing XenServer - It is important to monitor and configure XenServer to maintain optimal performance of the virtualized environment. Using the monitoring tools and utilities of XenCenter and configuring Workload Balancing, you can ensure that XenServer hosts, virtual machines, and storage repositories are performing at optimal levels.
Performance Monitoring - XenServer Performance Monitoring for Scalability Testing - http://support.citrix.com/article/CTX124157
Monitoring alerts can help signal system overutilization and potential performance bottlenecks. Two common means of monitoring the performance of XenServer are using XenCenter and running scripts from the XenServer command-line interface.
Using XenCenter to Collect Performance Data - XenCenter is a GUI which is used to monitor important system resources on the XenServer hosts and hosted virtual machines. XenCenter can give you an overview of system performance but has the following limitations:
- Data cannot be readily exported
- Granularity cannot be easily changed
- Some types of information are not gathered
To achieve these goals, you should use the XenServer command-line interface and create custom scripts.
Using the XenServer Command-Line Interface for Performance Data Capture - The XenServer command-line interface allows you to query the hypervisor for performance information and allows you to use standard Linux tools and utilities to gather performance data. This is especially useful during performance and scalability testing.
Installation Methods - You can install XenServer using an installation CD or by setting up a network-accessible TFTP server to deliver the installation files to PXE-capable XenServer hosts. The installation CD contains the necessary packages to set up the XenServer host and to create Windows virtual machines.
Note: A TFTP installation would be preferable in a situation in which hosted datacenters do not always have access to CD-ROMs.
XenServer Storage - Introduction to Storage Technologies - http://support.citrix.com/article/CTX118397

Intellicache - Using XenServer with IntelliCache reduces the cost of hosted XenDesktop deployments by enabling the use of a combination of shared storage and local storage. It works by caching data from a virtual machine's parent VDI in local storage on the virtual machine host. This local cache is then populated as data and read from the parent VDI. When many virtual machines share a common parent VDI, the data pulled into the cache from one virtual machine can be used by another virtual machine. Therefore, further access to the master image on shared storage is not required.
The requirements for using IntelliCache are:
- A thin-provisioned, local storage repository, which is configured during XenServer installation by selecting Optimized storage on XenDesktop for thin provisioning
- An NFS- or EXT-based shared storage to host the source virtual disk image
Note: Using IntelliCache prevents XenServer hosts in the environment from using XenMotion. This feature is only supported when using XenServer with XenDesktop - XenServer 6.0 Installation Guide - http://support.citrix.com/article/CTX130421
Security Considerations - It is common for the network interfaces on a XenServer host to be configured separately for the administration, storage, and virtual machine networks. You should consider the following security modifications for each of these networks:
- Administration Network: XenCenter exclusively uses port 443 to ensure that all traffic to and from the XenServer host is SSL encrypted. Third-party XenAPI clients can be configured to use port 80, which is not encrypted. To ensure that all traffic is encrypted, add firewall rules to the administration router to block external requests from port 80 to the XenServer host.
- Storage Network: Storage traffic for IP-based solutions, such as NFS or iSCSI, is not encrypted and travels through the control domain. Traffic on the storage network should be isolated from the administration network by configuring the storage network on a separate network interface, or separate VLAN.
- Virtual Machine Network: Virtual machine traffic should be isolated from management traffic and storage traffic whenever possible. This can be done with physical NIC separation or VLAN separation.
License Configuration - XenServer supports Citrix centralized licensing for all paid editions of the product License allocation is managed centrally and enforced by a standalone Citrix License Server. You can centralize licensing for all Citrix products, and. through the License Management Console, view the entitlement and current allotment of licenses for all Citrix products. For more information about XenServer licensing, see CTX125301
Optimizing XenServer - It is important to monitor and configure XenServer to maintain optimal performance of the virtualized environment. Using the monitoring tools and utilities of XenCenter and configuring Workload Balancing, you can ensure that XenServer hosts, virtual machines, and storage repositories are performing at optimal levels.
Performance Monitoring - XenServer Performance Monitoring for Scalability Testing - http://support.citrix.com/article/CTX124157
Monitoring alerts can help signal system overutilization and potential performance bottlenecks. Two common means of monitoring the performance of XenServer are using XenCenter and running scripts from the XenServer command-line interface.
Using XenCenter to Collect Performance Data - XenCenter is a GUI which is used to monitor important system resources on the XenServer hosts and hosted virtual machines. XenCenter can give you an overview of system performance but has the following limitations:
- Data cannot be readily exported
- Granularity cannot be easily changed
- Some types of information are not gathered
To achieve these goals, you should use the XenServer command-line interface and create custom scripts.
Using the XenServer Command-Line Interface for Performance Data Capture - The XenServer command-line interface allows you to query the hypervisor for performance information and allows you to use standard Linux tools and utilities to gather performance data. This is especially useful during performance and scalability testing.
Workload Balancing - You can configure Workload Balancing to optimize workloads for resource performance or to maximize the number of virtual machines on a XenServer host. These optimization modes can be configured to change automatically at predefined times or to remain the same at all times - Maximize Performance / Maximize Density / Fixed Optimization / Scheduled Optimization
Configuring XenServer Workload Balancing Settings Using XE Commands - http://support.citrix.com/article/CTX125186
How to Verify Workload Balancing Windows Installation - http://support.citrix.com/article/CTX124482
Workload Reports - The Workload Balancing server can generate reports about the performance of the virtualized environment.
The two most commonly used reports are:
- Workload reports, which allow you to audit servers, optimize servers, review virtual machine movement history, or monitor the health of the server or resource pool
- Chargeback reports, which allow you to measure virtual machine usage.
Configuring XenServer Workload Balancing Settings Using XE Commands - http://support.citrix.com/article/CTX125186
How to Verify Workload Balancing Windows Installation - http://support.citrix.com/article/CTX124482
Workload Reports - The Workload Balancing server can generate reports about the performance of the virtualized environment.
The two most commonly used reports are:
- Workload reports, which allow you to audit servers, optimize servers, review virtual machine movement history, or monitor the health of the server or resource pool
- Chargeback reports, which allow you to measure virtual machine usage.

