Common Disk Types:
SATA - Serial Advanced Technology Attachment (100 IOPS)
SCSI - Small Computer System Interface (150 IOPS)
SAS - Serial Attached SCSI [aka Next-Gen SCSI] (200 IOPS)
SSD - Solid State Disk (1000's IOPS)
IOPS - Input Output Operations per second
Partition Table Format
- Master Boot Record (MBR)
Partition table format from 1980's
Supports partitions up to 2 TB
Can support a max of 4 primary partitions
- GUID Partition Table (GPT)
Successor to MBR
Supports partitions up to 18 EB
Can support a max of 128 partitions per disk
File Systems
FAT - File Allocation Table
- Basic file system
- Partition size limits 2GB, 8TB (FAT32), 128 PB (exFAT)
- Basis for FAT32 & ex FAT - exFAT vs. FAT32 Comparison
NTFS - NT File System - OS Disk MUST be NTFS
- Support for metadata Auditing & journaling
- Security control & Encryption
ReFS Resilient File system (with Server 2012)
- Backward compatible with NTFS
- Support for larger files and volumes
NTFS or ReFS?
- Active Directory Domain Services & File Replication Service (NTFS)
- Volume Shadow Copy Service (NTFS)
- DFS - Distributed File System (NTFS)
- Hyper-V Servers (ReFS)
- Storage Spaces Direct (ReFS)
RAID - redundant array of independent disks
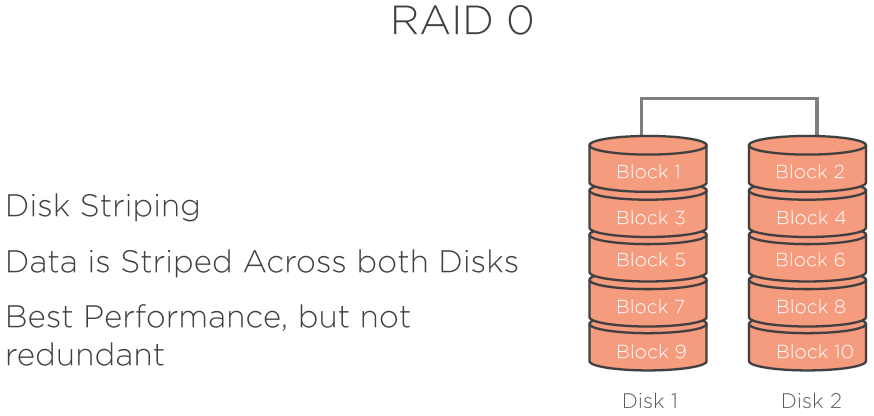
- RAID 0 - Striping
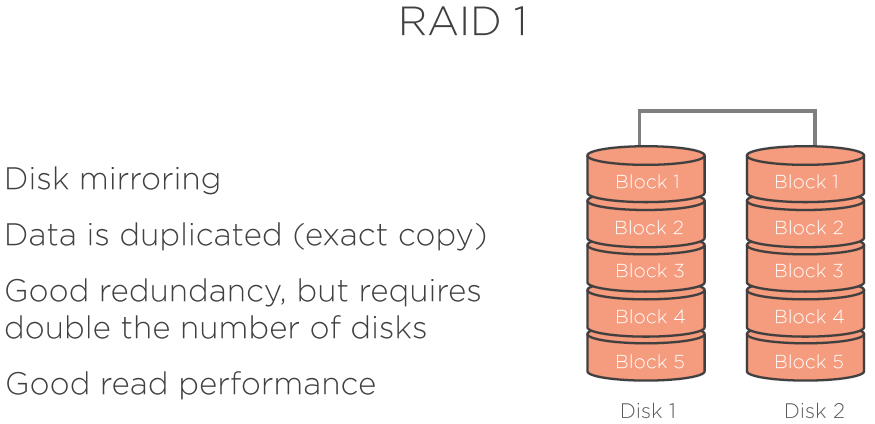
- RAID 1 - Mirroring
- RAID 5 - Striping with Parity
Disk Types
- Basic
- Dynamic (allows Disk to span multiple volumes)
RAID Setups explained

SATA - Serial Advanced Technology Attachment (100 IOPS)
SCSI - Small Computer System Interface (150 IOPS)
SAS - Serial Attached SCSI [aka Next-Gen SCSI] (200 IOPS)
SSD - Solid State Disk (1000's IOPS)
IOPS - Input Output Operations per second
Partition Table Format
- Master Boot Record (MBR)
Partition table format from 1980's
Supports partitions up to 2 TB
Can support a max of 4 primary partitions
- GUID Partition Table (GPT)
Successor to MBR
Supports partitions up to 18 EB
Can support a max of 128 partitions per disk
File Systems
FAT - File Allocation Table
- Basic file system
- Partition size limits 2GB, 8TB (FAT32), 128 PB (exFAT)
- Basis for FAT32 & ex FAT - exFAT vs. FAT32 Comparison
NTFS - NT File System - OS Disk MUST be NTFS
- Support for metadata Auditing & journaling
- Security control & Encryption
ReFS Resilient File system (with Server 2012)
- Backward compatible with NTFS
- Support for larger files and volumes
NTFS or ReFS?
- Active Directory Domain Services & File Replication Service (NTFS)
- Volume Shadow Copy Service (NTFS)
- DFS - Distributed File System (NTFS)
- Hyper-V Servers (ReFS)
- Storage Spaces Direct (ReFS)
RAID - redundant array of independent disks
- RAID 0 - Striping
- RAID 1 - Mirroring
- RAID 5 - Striping with Parity
Disk Types
- Basic
- Dynamic (allows Disk to span multiple volumes)
RAID Setups explained




